Research Interests
Our research group has interest on the synthesis of potential drug candidates by the development of new synthetic routes using mild, inexpensive and greener conditions.
Watch a sample movie about the Green Synthesis of D-ribonolactone from D-ribose using bromo salts.
1 Sythesis of chiral ϒ-lactames
Recently, our group published1 the preparation ϒ-lactames obtained by reaction of chiral vinyl sulfilimines with dichloroketene in a process called ϒ-lactamization. This reaction produced up to two new stereocenters starting from a quiral sulfliminine. (Scheme 1)
Scheme 1. First example of a chiral lactamization.
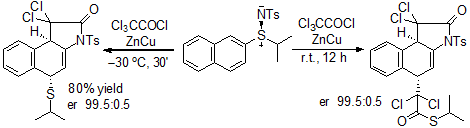
1. Silveira, G. P.; Marino, J. P. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 3379.
Total synthesis of alkaloids
A principle alkaloid of the Calabar bean, (–)-physostigmine (1), is used therapeutically for the treatment of myasthenia gravis and glaucoma, and analogues of physostigmine show promise for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. The recent discovery of an effective method for ϒ-lactamization, by the reaction of vinylsulfilimines with dichloroketene, suggested a concise route to the asymmetric synthesis of (–)-physostigmine (scheme 2):
Scheme 2. Concise synthesis of the natural product physostigmine.
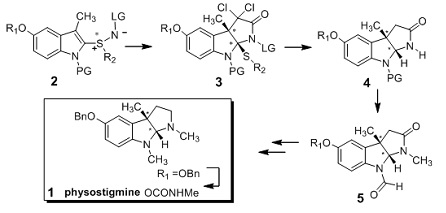
The protected indolylsulfilimine 2, made by functionalization of an appropriately protected indole with a chiral sulfilimine, reacts with dichloroketene to give dichlorolactam 3 in 70% yield. Removal of the chloro, thioether, and leaving group is accomplished in a single step (nBu3SnH, AIBN) to afford the lactam 4. Exchange of the indole protecting group with an N-formyl, followed by lactam N-methylation, gives key intermediate 5, which previously was transformed into the natural physostigmine (1).
2. Allylic thiocyanates as a new class of antitubercular agents
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). This dreadful disease has been responsible for the deaths of over one billion people and currently infects one-third of the world's population. Our laboratory, in collaboration with Prof. Sá research group which has had a long research interest in the Morita-Baylis-Hillman (MBH) reaction, preparared of various allylic azides, thiocyanates, isothiouronium salts, and N,N'-diacetylisothioureas in aqueous medium as versatile scaffolds for synthesis (Scheme 3). Thus, five new and promising compounds having good (micromolar) to excellent (sub-micromolar) potency against replicating Mtb H37Rv were identified.2
Scheme 3. New methodology for the synthesis of depsipeptides.
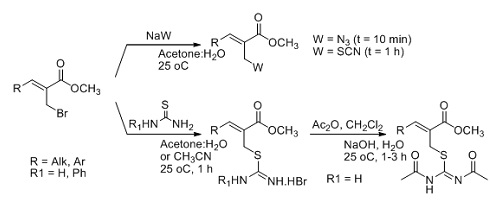
2. Silveira, G. P.; Ferreira, M.; Fernandes, L.; Moraski, G. C.; Cho, S.; Hwang, C.; Franzblau, S. G.; Sá, M. M. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 6486.
3. Strategies to bypass vancomycin-resistant bacteria – development of new antibiotics.
Preparation of depsipeptides as a model to mimic altered cell wall peptidoglycan precursor ending in D-Ala-D-Lac
Bacterial infections resistant to potent antibiotics like vancomycin present serious threats to public health. One of the promising strategies to bypass resistance includes the selective and catalytic cleavage of the D-Ala-D-Lac depsipeptide present in the altered termini of cell wall peptidoglycan precursors.
In vitro and in vivo cleavage of D-Ala- D-Lac by small molecules reduced the concentration of the precursor with altered termini re-sensitizing vancomycin-resistant bacteria. However, the reported synthesis of p-NO2PhCO-D-Ala-D-Lac required for kinetic studies involved five steps and a rather difficult reaction condition precluding its large-scale preparation.
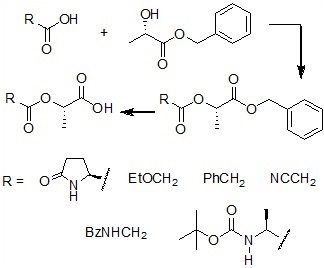
In this way, representative models for depsipeptides were readily obtained by a two-step procedure using mild conditions and easily accessible reagents: esterification of inexpensive (S)-lactic acid, couple of the resulting ester with the proper a-functionalized acid, and deprotection (scheme 4).
Scheme 4. New methodology for the synthesis of depsipeptides.
Synthesis of a group of nucleophilic compounds for hydrolytic cleavage of selected targets
As part of this work, hydrolytic compounds were synthesized in order to obtain potent nucleophiles for selective ester cleavage of the depsipeptides targets presented. These molecules were designed using Molecular Modeling indicating that the presence of a basic center (such as amine) tethered to a nucleophilic group (such as hydroxylamine) would increase their nucleophilicity by an intramolecular basic assistance (Scheme 5). The molecules would have an affinity for the Ala-Lac targets by an extra interaction of the basic group with the acidic carboxyl group.
Scheme 5. Nucleophilic compounds for hydrolytic cleavage to the Ala-Lac targets.
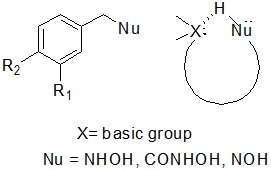
4. Metal-free artificial nucleases based on simple oxime and hydroxylamine scaffolds
Hydroxylamines, oximes and analogues are nucleophilic molecules that have found broad application as biological tools. Particularly, it has been found that simple alkyl hydroxylamines are potent cleaving agents of phosphodiesters and related model compounds.
Therefore, we envisaged that oximes and hydroxylamines might be also interesting candidates for cleaving phosphate bonds in nucleic acids.3
3. Silveira, G. P.; Sa, M. M.; Fernandes, L.; Nome, F.; Terenzi, H.; Fischer, F. L.; Ribeiro, C. W. Bior. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 4499.
5. Synthesis of carbohydrate derivatives as inhibitors of the enzyme gGAPDH (T cruzi - Chagas disease)
In an ongoing program working towards the synthesis of nucleosides and carbohydrates as inhibitors of trypanosomal gGAPDH enzyme, we required selective substituted ribose derivatives in a way of evaluating their inhibitory activities.
Thus, methodologies using mild conditions and inexpensive reagents were developed for synthesis of carbohydrate derivatives selectively acylated at 2'-, 3'- and 5'- positions4 (Scheme 6).
Scheme 6. Methodologies developed for the synnthesis of carbohydrate derivatives.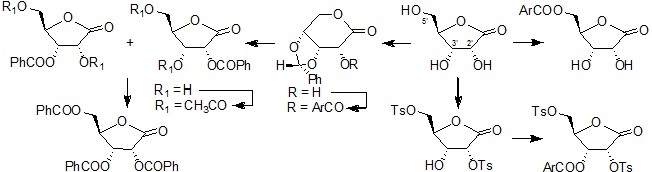
4. Sá, M. M.; Silveira, G. P.; Castilho, M. S.; Pavão, F.; Oliva, G. Arkivoc 2002, 8, 112–124.
Structural assignment supported by conventional NOESY-NMR and X-Ray analysis
Aldonolactones (modified sugars with the anomeric center in its higher oxidation state) have been widely employed in synthesis as an alternative to simple carbohydrates. D-Ribono-1,4-lactone (D-ribono-ϒ-lactone, 6) is one of the most useful chiral precursors from this class, although the issues associated with product characterization due to unpredictable transformations are also present to a great extent. For instance, the product obtained from the reaction of D-ribono-1,4-lactone (6) with benzaldehyde in acidic medium, which was initially assigned as being 3,5-Ο-benzylidene-D-ribono-1,4-lactone (7), had the correct structure unequivocally established as 3,4-Ο-benzylidene-D-ribono-1,5-lactone (8) by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis of its Ο-acetyl derivative. A complex rearrangement involving acetal migration and ring expansion sequences has been proposed for this transformation. Therefore, the scope of D-ribono-1,5-lactone 8 and analogues as chiral building blocks relies on the development of more convenient methods for structural assignment, particularly those based on more conventional NMR techniques.
Scheme 7. Ribonolactones of 5-, and 6-members ring.
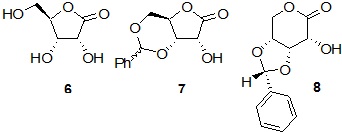
Finally, a simple and efficient method was developed5 for structural assignment of benzylidene-D-ribono-1,5-lactones by 1H-NMR experiments involving NOESY measurements in solution (scheme 8).
Scheme 8. Simple and eficient method for structural assignment of ridonolactones.

5. Silveira, G. P.; Sa, M. M.; Caro, M. S. B.; Ellena, J. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2008, 19, 18.
